Analytics
Data formats
https://www.datanami.com/2018/05/16/big-data-file-formats-demystified/
- Parquet
- Columnar format
- Schema is included
- ORC (optimized row columnar)
- Columnar format
- Avro: JSON with schema
- Row format - JSON like
- More for Kafka where it is heavy on writes
- Same
- Optimized for storage + compression (optimize cost)
- Machine-binary readable format, so it can be split between disks and processed in parallel
- Contain the schema within its content, so it is self described
- On-the-wire format (?)
- Context
- Columnar format is best for heavy read aggregate analytics. Row based format are good for writes
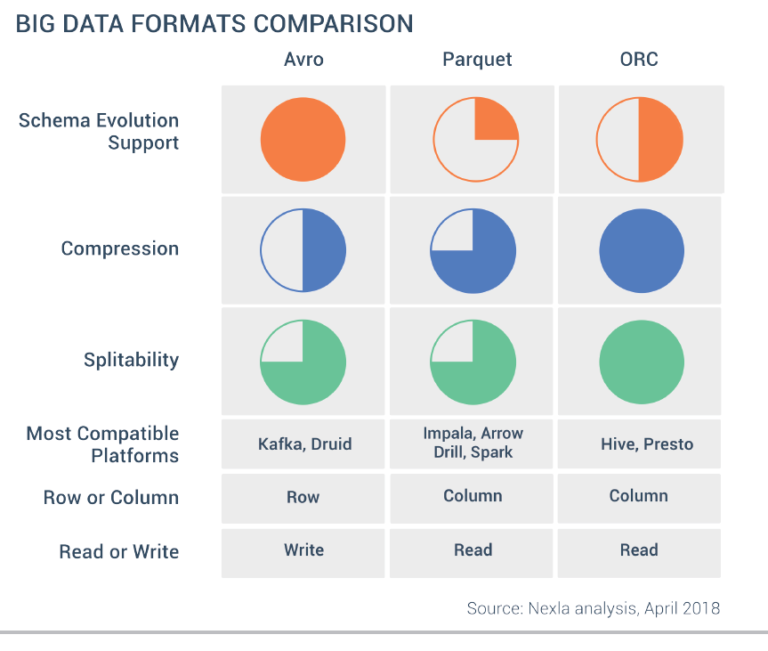
- Columnar format is best for heavy read aggregate analytics. Row based format are good for writes
- Other formats
- CSV/JSON/XML
Database types
RDBMS
NoSQL
- Types
- Key-value
- Document oriented
- Graph DBs
- Samples: Firestore (DataStore), Bigtable, DynamoDB, MongoDB, Cassandra
Data warehouse
Data warehouse = Storage + Compute
Schema type
Star Schema
- 1 Fact table + dimension tables
- Dimension table is 1-dimensional table
- Joins use foreign keys
- Pros:
- Faster query
- Easy to understand
- BI supports
- Suitable for data marts
- Cons:
- Dimension tables are nor normalized
Snowflake Schema
- Multi-dimensional tables
- Dimension tables are normalized (i.e. has additional dimension tables)
- Pros:
- Smaller disk space
- Easy to add/remove dimension
- No redundant data
- Suitable for data warehouse
- Cons:
- Query performance is slower
- More maintenance for dimension tables
Galaxy Schema
- Multiple fact tables are dimension table
Star Cluster Schema
- Full hierarchy - joins fact tables (e.g. Customer, Product and Transaction)
BigQuery
Migration
- Migrate data
- Options: bq command, through GCS, or BigQuery Data Transfer Service
- BigQuery Data Transfer Service
- Support Google’s sources, S3, Redshift, Teradata
Value props
Use cases
Compete
Dataproc (~EMR)
Fully managed open-source BIG data and analytics processing service.
- Can spin up Apache Spark or Apache Hadoop clusters in 90 seconds
- Clusters are auto-scaled
- Can install other OSS (open source service) such as Flink, Presto, and Hive.
Background
MapReduce
- Programming model: Map and Reduce functions
- Map: input to key-value
- Reduce: merge maps with the same key
Hadoop
- Set of softwares (HDFS, MapReduce, and YARN) enable the cluster to store and process data
- HDFS: H distributed file system
Apache Pig: high-level framework to run MapReduce on Hadoop
- Platform for analyzing large datasets
- Pig Latin (the language) defines analytics jobs: Merging, Filtering, Transformation
- Abstract of MapReduce
- ETL tool
- Compiled to MapReduce
Apache Spark: fast memory storage; parallel processing
- Improve limitations of MapReduce (linear)
- Distributed data multisets across cluster
- Core modules
- Spark SQL
- Spark Streaming
- MLLib: ML
- GraphX
- Low latency, higher cost vs. Hadoop
Apache Kafka: distributed streaming platform
- Publish/subscribe
- Producer / Consumer / Streams / Connector
- Partition (across nodes)
- Topic across partition
- Zookeeper
- Guaranteed ordering
- Pull (poll) only
Big data
- Hadoop: mostly for batch processing
- Spark: batch + stream processing (part of Hadoop ecosystem)
- Flink: single run-time for streaming and batch processing
Data preparation (data wrangling)
- Profiling > Cleaning > Transforming > Enriching
- vs ETL: Data prep is more suitable for non-tech vs. ETL is more tech (python/R)
ETL
- Feed data to data warehouse (DWH)
ELT
- Utilize the power of the warehouse storage (e.g. BigQuery)
Migration
- Data
- Data type, model
- ETL
- BI/Reports
- Downtime
Techniques
- Slicing and dicing
- Filter/reduce the data to insights
- Data is presented as cube (multi-dimensional)
- OLAP, ROLAP (relational OLAP)
Misc
- Bigtable vs. BigQuery? [A] BigQuery is more for data that is not changed (i.e. data warehouse, data is appended, is not changed by content itself). Bigtable is a database for analytics (vs. Datastore), and it supports read/write activities.